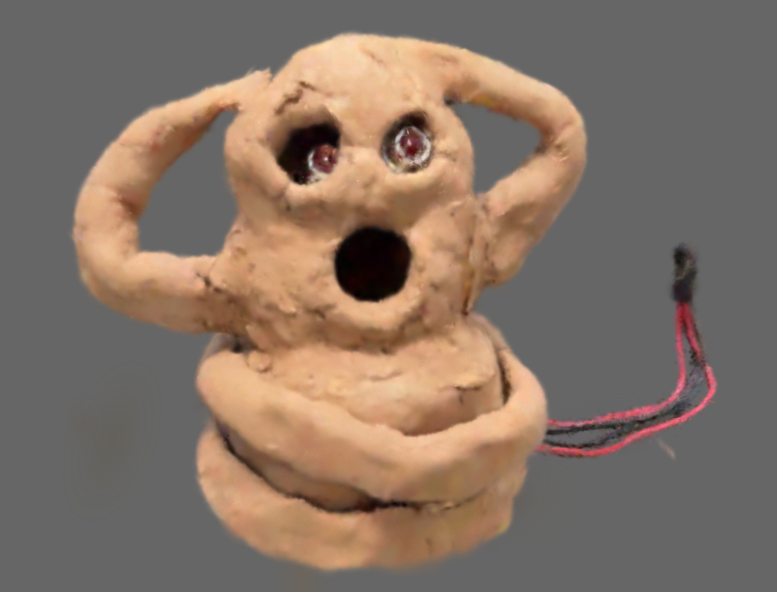
A Python library to convert 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) format data to CSV format, edit it, and convert it back to 3DGS format.
- Convert 3DGS format (PLY) data to CSV format
- Convert CSV format data to 3DGS format (PLY)
- Convert 3DGS format to standard point cloud format
- Convert point cloud data to/from CSV format for easy editing
- Tools for comparing 3DGS files and analyzing differences
- Merge multiple 3DGS files into a single scene
- Apply transformations (translation, scaling) to 3DGS files
- Verified compatibility with SuperSplat for visualization
- Point cloud data verified with CloudCompare
- src/: Core functionality for converting between formats
- tools/: Additional utilities for analyzing and comparing 3DGS files
- examples/: Sample code demonstrating usage of the library
- images/: Sample images and visualizations
The core library in the src/ folder requires numpy for numerical operations. This dependency is automatically installed when you install the package.
The tools in the tools/ folder require additional dependencies:
pip install pandas matplotlibThese are automatically installed if you install the package with the [tools] extra.
# Basic installation with core functionality
pip install 3dgs-edit-tools
# Complete installation with tools for analysis and comparison
pip install 3dgs-edit-tools[tools]Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/404background/3dgs-edit-tools.git
cd 3dgs-edit-tools
pip install -e . # Install in development modeThis library uses CSV format as an intermediate step for editing 3D Gaussian Splatting data because:
- Human-Readable: CSV files can be easily viewed and edited with spreadsheet software or text editors
- Ease of Editing: Unlike binary formats, CSV files allow direct modification of values without specialized tools
- Compatibility: CSV is widely supported by data processing tools and programming languages
- Transparency: The structure and values are visible, making it easier to understand the data
Point cloud data is also converted to CSV format before editing to maintain the same benefits.
from src import convert_3dgs_to_csv, convert_csv_to_3dgs
# Convert PLY file to CSV
csv_path, _ = convert_3dgs_to_csv('model.ply')
# Write your code to edit the CSV file here
# ...
# Convert edited CSV back to PLY
restored_ply = convert_csv_to_3dgs(csv_path, None)from src import merge_3dgs_files, create_transformed_copy
# Create a transformed copy with 10cm translation on X-axis
transformed_ply = create_transformed_copy('model.ply', 'model_moved.ply',
{'translate': [0.1, 0, 0]})
# Merge original and transformed models
merged_ply = merge_3dgs_files('model.ply', transformed_ply, 'merged_scene.ply')from src import (
convert_3dgs_to_pointcloud,
convert_pointcloud_to_3dgs,
convert_pointcloud_to_csv,
convert_csv_to_pointcloud
)
# 3DGS to point cloud
pointcloud_path = convert_3dgs_to_pointcloud('model.ply')
# Point cloud to CSV for easy editing
csv_path = convert_pointcloud_to_csv(pointcloud_path)
# Edit CSV file here...
# CSV back to point cloud
edited_pointcloud = convert_csv_to_pointcloud(csv_path)
# Point cloud back to 3DGS
restored_model = convert_pointcloud_to_3dgs(edited_pointcloud, 'model.ply')To use the comparison tool for analyzing differences between 3DGS files:
# First install required dependencies
pip install pandas matplotlib
# Run the comparison tool
python -m tools.compare_gs path/to/original.ply path/to/modified.ply --output-dir comparison_resultsFor more information about available tools, see the tools/README.md file.
After installation, the package provides several command-line executables for easy use:
Convert PLY to CSV:
3dgs-to-csv input.ply --output_csv output.csvConvert CSV to PLY:
csv-to-3dgs input.csv --output_ply output.plyConvert 3DGS to point cloud:
3dgs-to-pointcloud input.ply --output_ply output_pointcloud.plyConvert point cloud to 3DGS:
pointcloud-to-3dgs input_pointcloud.ply original.ply --output_ply restored.plyMerge two 3DGS files:
merge-gs file1.ply file2.ply --output merged.ply --translate-x 0.1Convert 3DGS to mesh:
3dgs-to-mesh input.ply --output output_mesh.obj --method hybrid --quality highConvert point cloud to CSV:
pointcloud-to-csv ply2csv input_pointcloud.ply --output_csv output.csvConvert CSV to point cloud:
csv-to-pointcloud input.csv --output_ply output.ply --color_type ucharCompare two 3DGS files:
compare-gs original.ply modified.ply --output-dir comparison_resultsSample code is available in the examples folder. See examples/README.md for details.
This project has been tested with the following visualization tools:
- SuperSplat: For 3D Gaussian Splatting format files (.ply)
- CloudCompare: For point cloud format files (.ply)
- Blender: For mesh format files (.obj, .ply, .stl)
All point cloud data conversions have been extensively tested using CloudCompare to ensure proper structure, color representation, and export compatibility. Mesh outputs have been verified with Blender to confirm proper mesh topology and compatibility.
Converts 3DGS format (PLY) data to CSV format.
Arguments:
ply_filename(str): Path to the input PLY filecsv_filename(str, optional): Path to the output CSV file. If not specified, it's automatically generated from the input filename
Returns:
- tuple: (csv_filename, None) - Paths of the generated files
Converts CSV format data to 3DGS format (PLY).
Arguments:
csv_filename(str): Path to the input CSV filefooter_filename(str, optional): Path to the file containing footer data. If not specified, it's automatically generated from the input filenameoutput_ply_filename(str, optional): Path to the output PLY file. If not specified, it's automatically generated from the input filename
Returns:
- str: Path of the generated PLY file
Merges two 3D Gaussian Splatting files into a single file.
Arguments:
file1(str): Path to the first 3DGS filefile2(str): Path to the second 3DGS fileoutput_file(str, optional): Path to the output merged 3DGS filetransform(dict, optional): Transformation to apply to the second file (e.g.{'translate': [0.1, 0, 0]})
Returns:
- str: Path of the generated merged 3DGS file
Creates a transformed copy of a 3DGS file with specified transformations.
Arguments:
input_ply(str): Path to input PLY fileoutput_ply(str): Path to output transformed PLY filetransformation(dict): Dictionary with transformation parameters (e.g.{'translate': [0.1, 0, 0], 'scale': [1.5, 1, 1]})
Returns:
- str: Path to transformed PLY file
Converts 3D Gaussian Splatting format to standard point cloud PLY format.
Arguments:
ply_filename(str): Path to the input 3DGS PLY fileoutput_ply_filename(str, optional): Path to the output point cloud PLY file
Returns:
- str: Path of the generated point cloud file
Converts a point cloud file back to 3D Gaussian Splatting format using an original 3DGS file as reference.
Arguments:
pointcloud_ply(str): Path to the input point cloud PLY fileoriginal_3dgs_ply(str): Path to the original 3DGS file to use as referenceoutput_ply(str, optional): Path to the output 3DGS file
Returns:
- str: Path of the generated 3DGS file
Converts point cloud PLY file to CSV format for easier editing.
Arguments:
ply_filename(str): Path to the input point cloud PLY filecsv_filename(str, optional): Path to the output CSV file
Returns:
- str: Path of the generated CSV file
Converts CSV file to point cloud PLY format.
Arguments:
csv_filename(str): Path to the input CSV fileoutput_ply_filename(str, optional): Path to the output point cloud PLY filecolor_type(str): Type of color data to use in PLY file ('float' or 'uchar')
Returns:
- str: Path of the generated PLY file
This project is released under the MIT License. See LICENSE file for details.